Cells are the basis for all living things. They provide structure and carry out functions necessary for survival. Recent studies have been conducted on the brain, examining the function of the 3,000+ cells found in the human brain. They found the brain to be extremely complex and have found the following: how brains vary among people and the similarities and differences between humans and primates.
Unique Brains
Researchers looked at 100 different cells from different brain regions and found cells called astrocytes that use their genes differently based on where they are located. For example, they can regulate blood flow, but also send mitochondria to neurons. They found staggering similarities between 75 brain cells, but they also found differences. It is widely accepted that eukaryotic cells are broken into different divisions to promote productivity. All human brain cells are similar, having an endomembrane system. The staggering similarity is that all cells will consist of a nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and mitochondria. This endomembrane system allows parts of the cell to be specialized in a specific function, increasing productivity. Being that cells have different functions, however, cells’ components vary. For example, the brain immune cells, microglia, have unique genes that they use from person to person.
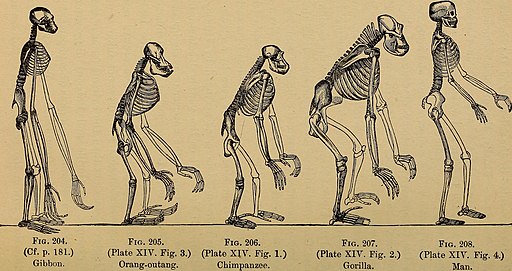
Human Relationship to Primates
Researchers found that cells in the frontal cortex “didn’t differ a lot between primate brains”. While similar, human brains use genes differently from primate brains. Particularly, how cells communicate. It appears that hundreds of genes carry out “human-specific” functions. It is not yet clear as to what exactly these genes carry out.
These new findings are significant for the biological and neurological community, for they add more evidence towards understanding the complexity of the human brain. You may be asking why this matters if there are no definitive answers? Well, we are one step closer to finding an answer. Neuroscience is relatively new. Understanding astrocytes is vital to understanding brain malfunctions. Doctors and scientists will be able to know where the issue is occurring if they understand the anatomy and functions of the brain. Finally, deciphering the similarities and differences between the human brain and primate brain contributes to strengthening Darwin’s evolutionary theory. Given the staggering similarities, the theory seems valid. Scientists noting there are human specific genes suggest why humans are in fact different and more advanced from primates. It is important to stay patient with research for cells, for even small developments are powerful. For example, the Endosymbiont Theory is a dominant theory that also began with seemly small data and breakthroughs.
I find the make up of the human brain fascinating. It’s brilliant how we all share similar brain cells so that we can all function relatively the same. It is truly extraordinary that we all have certain cells in certain spots to conduct different functions. Did you know that simply the location of a cell impacts its entire function? Additionally, the more connections we find between our brains and primate brains, the more likely evolution seems. I am a believer in evolution due to the staggering similarities in our DNA and make up. We share 98.8% of our DNA with chimpanzees! What do you think: did we evolve from apes?



Leave a Reply