In the article titled, Scientists discover the possible triggers for bacterial pathogens, opening the door for new treatment strategies, the reporter discusses how Alexander Fleming’s unintentional discovery represented a crucial turning point in medical history and sparked the creation of several additional antibiotics, saving countless lives in the process. This famous Scottish pharmacist discovered penicillin, the first antibiotic, in 1928 and since then many others have followed in his footsteps. Additionally, his discoveries led to the idea that “extraordinary appearances” should not be ignored. His famous sentiments hold true to multiple scientific discoveries; this is including a group of scientists at UNLV who are studying shigella.

In the picture above you can see Shigella in a stool sample.
Shigella is a harmful bacteria that can cause many issues in the human body such as stomach cramps, fever, diarrhea (which is frequently bloody), and can also be fatal. Shigella infection is an intestinal ailment caused by a family of bacteria called shigellosis. Shigella spreads quickly. When individuals come into touch with and ingest quantities of germs from an infected person’s feces, they get infected with shigella.
Initially I was not engaged with this topic because I had no idea how it could be relevant to my life. However, my recent work as an EMS volunteer has proved me wrong. Although I have not seen a patient who had shigella, I have observed many other patients who experienced similar bacterial diseases and am eager to find the best way to treat them.
Moreover, these scientists are focused on the proteins in shigella that are called VirB. VirB proteins act as a switch in the bacteria and bind to Shigella by interacting with Shigella’s DNA. This interaction between VirB and Shigella’s DNA is a key step in the process that activates the bacterium’s virulence genes. Essentially, the DNA is what causes disease in people. Researchers found that by interfering with the way VirB bonds to the shigella, they can minimize the effects it has on humans.
Furthermore, this research is largely important to the understanding of how proteins such as VirB are able to turn harmless bacteria into deathly ones. Moreover, this insight is also helpful in the development of treatments for other diseases such as Campylobacteriosis, E coli, and Cholera which are caused by similar proteins in different bacterias.
After studying Organic Compounds in my AP Biology class, I was able to make connections to the material we have learned such as the different protein structures which heightened my interest in this topic even more. The reason that similar proteins are able to cause so many different diseases is because of the altercation in protein shape as well as body response. All proteins have specific shapes and structures that determine how the protein will interact with the human body. Additionally, there are four main protein structures including primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary which all play a role in how proteins behave. Moreover, all proteins have side chains which provide characteristics and make them different from one another. The side chains in proteins give amino acids characteristics and by changing one small detail you will change the structure (shape) of the protein and thus how it interacts with the human body.
To continue, E coli is a type of bacteria frequently discovered in both the human and animal intestines. Since it aids in digestion and the creation of several vitamins, it is often safe and even advantageous. However, some E. coli strains have the potential to be dangerous and contagious.
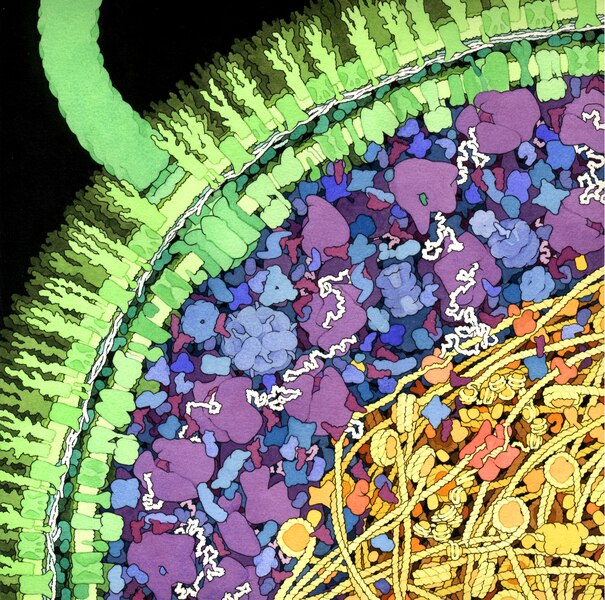
The photo above shows a cross section illustration of an E.coli cell.
However, the most important factor in this research is a molecule known as CPT, which is short for Camptothecin. Camptothecin was first identified as a topoisomerase inhibitor in 1966. Topoisomerases are nuclear enzymes involved in DNA replication (and more). To understand its role, you can think of Camptothecin as a key part in a puzzle involving Shigella. VirB acts as a switch to turn on the bacterium’s ability to cause disease in the human body. For this switch to work correctly, it needs Camptothecin. Camptothecin is the key that enables VirB to bind to Shigella’s DNA, which then activates the disease-causing process.
The researchers are interested in interfering with this binding process. By doing so, they aim to prevent Shigella from making people sick. This line of research isn’t just about Shigella. The hope is that the knowledge gained from studying this process could be applied to finding a solution for a whole group of diseases caused by different bacteria similar to Shigella.
So… what are YOUR thoughts on the research of Camptothecin’s role in Shigella’s causing a process that could lead to the investigation of new treatment? Are you optimistic about the potential impact on the future public health?






 (PF4)
(PF4)

Sandovalosome
"Hey, Summercules! I enjoyed learning more about Tardigrades now that we've discussed them ..."
Sandovalosome
"Hi Nucliyatide! I am guilty of getting UV gel manicures. I hate to ..."
Sandovalosome
"Hey Zaygote, nice title! It's a great name to sum up your blog, ..."
Sandovalosome
"Hi Nucliyatide! Your post caught my attention because I have recently started drinking ..."
benzyme
"Whoa, Jamesome! I have been antigen-tested for COVID-19 as an individual before and ..."
benzyme
"Hi Slayerson, thank you for sharing this Influenza antiviral information and shedding light on ..."
benzyme
"Hi Nucliyatide, thank you for sharing your research on this topic of diet vs ..."
benzyme
"Hi Summerculs, I have not personally encountered COVID-19 leading to brain fog before, so ..."
ariatom
"Hi Nucliyatide! Thank you for sharing light on this myth! I used to ..."
ariatom
"Hi Zaygote! It would be so nice to be active and lively in ..."
ariatom
"Hi AtomicMass! You're right, it's so cool how bacteria fossils can show the ..."
ariatom
"Hi Saratonin! Thank you for expressing the dangers of fentanyl by showing the ..."
lagoon1
"Atomicmass, I enjoyed reading your post about proteins and infection. I found it ..."
lagoon1
"Summerculs, I enjoyed hearing the multiple stories you have in your post. The ..."
lagoon1
"I never put much thought into the differences between the COVID-19 vaccines. After ..."
lagoon1
"Sandovalosome your post about the Optical Frequency Comb was very interesting in relation ..."
katealyst
"Hi Alexoskeleton! Thank you for pointing out that there have been 50 mutations ..."
katealyst
"I am sorry. The first link of Weissman calling his mom should work ..."
katealyst
"Hi Benzyme! Thank you for sharing why Weissman and Kariko were so deserving ..."
katealyst
"Hi Lagoon1! I appreciate that you not only explained the connection between long ..."
katealyst
"Hi Summercules! Thank you for sharing that personal anecdote about your mom's COVID ..."
alindvall
"Hypotheoni, I'm currently enrolled in a graduate education course, and we were required to ..."
namurthy
"Hi Blakelement! The first line of your post was very attention grabbing! It ..."
namurthy
"Hi Lukewarm! That stats included in your post were shocking! It's crazy to ..."
namurthy
"Hi Lobiotic! I really like how your post connected to people in your ..."
namurthy
"Hi ITSALIVE! This is a really informative post about the higher rate ..."
jouleian
"Hi emdaniels, thank you for sharing this interesting research on the ability of ..."
jouleian
"Hi, avacuole, I just read your post about the research being done at ..."
jouleian
"Wow, this is a really interesting and informative post about the recent discovery ..."
jouleian
"This important research on the connection between SARS-CoV-2 and brain fog was very ..."
deukaryota
"Hi Namurthy, I loved reading your post because it was a very interesting ..."
deukaryota
"Hi Hypotheoni, I really enjoyed reading your post, and I loved how relevant ..."
deukaryota
"Hi Papanagopoulos- this is such an interesting discovery, and I loved how you ..."
deukaryota
"Hi Liobiotic- I loved reading you post. It is well written and ..."
enshowal42
"Jen, Thanks for the response. I really appreciate you sharing your assignment with ..."
jnewbio
"Thanks for your comment, Eric! I'm glad you discovered our blog, and ..."
enshowal42
"Hello! I am a student taking graduate classes working towards a masters degree ..."
sukrose
"Thank you, merrillenmeyerflask for your comment! That nasal spray is quite interesting! "
shallele
"I found this post incredibly interesting Hydropherick. My initial expectation was that the ..."
cytokinesav
"In a time where there is so much uncertainty regarding COVID's aftereffects, I ..."
cytokinesav
"Thank you for this insightful post. I appreciate how this entire post is ..."
cytokinesav
"Thank you for this post. I think the relation between physical and mental ..."
cytokinesav
"Thanks so much for sharing this with us. I knew global warming had ..."
cytokinesav
"Okay, wow! Fermented foods are big in Asian cultures. However, as an Asian ..."
shallele
"I enjoyed this post Rayceptor, but I was curious why you made no ..."
shallele
"I found the experiment with tadpoles particularly interesting. One thing I wonder is ..."
merrillenmeyerflask
"Hey Chrisynthesis, what an interesting and insightful article! I think that this ..."
merrillenmeyerflask
"Wow PhotoSamthesis! I never even knew that this was an option until now ..."
merrillenmeyerflask
"Really Interesting Post Clalvincycle, if all this AOS jargon has some real validity, ..."
shallele
"As someone who experiences fasting for 24 hours once a year for Yom ..."
clalvincycle
"Very interesting fertilivization. The idea of water proving that there is life on ..."
clalvincycle
"Great post. It’s interesting to see the many ways scientists are trying to ..."
clalvincycle
"Wow osmosisjohn, great post! It’s amazing to see how far technology has come. ..."
clalvincycle
"Great post marcochondria! As you mentioned before, it may be difficult for people ..."
lipidliv
"Great information! I feel so much more educated! As we have been learning ..."
lipidliv
"Thank you for sharing this insight on a new way to detect the ..."
lipidliv
"Thank you for the great article! In light of the recent jump in ..."
lipidliv
"Great post! I did some research of my own and I do agree ..."
lipidliv
"Thank you for sharing this information! I have done some additional research on ..."
biosyntaysis
"You have definitely convinced me to buy a yoga mat, charboncycle! Wow - ..."
biosyntaysis
"Fascinating post, Lucytoplasm! I have always been extremely interested in gut health as ..."
biosyntaysis
"Fascinating post, jervoussytem! I have always wondering what the impacts of fasting are ..."
biosyntaysis
"Thank you so much for this well-written, educational post, Cytokinesav! Cocaine usage is ..."
eukericotic
"I've been told many times that fermented foods are healthy for you, but ..."
eukericotic
"Even as a major environmentalist, I had never heard of this phenomenon before. ..."
eukericotic
"I found this look into these COVID variants very interesting and super important. ..."
eukericotic
"Cytokinesav, this is a really interesting topic to write about and I liked ..."
merrillenmeyerflask
"Well put Sukrose! I think it is important to appreciate all we've achieved ..."
merrillenmeyerflask
"Hey LuCytoplasm! Such an interesting post, I really like how you go into the ..."
mitochondriana
"Your article was really cool, Kangyotype! It's interesting to know that the ..."
mitochondriana
"This article is great! Very cool to know that most mammals think the ..."
mitochondriana
"I really like your article saadoplasm! I think that it definitely makes me ..."
mitochondriana
"I have to agree with saadoplasm, your heading, Ethansol, definitely caught my eye. ..."
mitochondriana
"What a cool article! It's interesting how impactful phosphorus and carbon are on ..."
saadoplasm
"I found an article about how memories of pain don't go away completely. ..."
saadoplasm
"I was definitely intrigued by this headline. I know that I like ..."
saadoplasm
"I came home one time and asked my mom if it was dangerous ..."
saadoplasm
"This is so crazy because just LAST NIGHT, my dad and I were ..."
saadoplasm
"I enjoyed this article because I guess I like a few posts about ..."
glovcose
"I found this post very interesting! It shows how, we as humans, are ..."
glovcose
"This post is really interesting and it really helps to show how advanced ..."
glovcose
"I found your post very interesting. It is shocking for me to see ..."
glovcose
"I found this article really interesting and it is really cool to see ..."
glovcose
"This article is very interesting and it really showed how beneficial carcasses are ..."
dannimal
"Thank you Largeintestein for this fascinating information about stevia. While most people here ..."
dannimal
"Like most other people commenting on this article, I am glad you have ..."
dannimal
"Wow I feel like I just read an excerpt from a science fiction ..."
dannimal
"Thank you for such a thought provoking article Andygen! I share yours and ..."
dannimal
"Thank you for bringing light to such a fascinating topic Ethansol! I had ..."
liambilicalcord
"Cool research! As a dog owner, my dad often asked about my dog ..."
liambilicalcord
"Interesting article Kangyotype! I was recently reading about a similar nuclear disaster that ..."
liambilicalcord
"Awesome article. The effects of humans on our environment are, in my opinion, ..."
actrevationenergy
"I think that it is really ground breaking that science has gotten to ..."
actrevationenergy
"This is the amazing part of the world that is never really talked ..."
trnayon
"Great blog post! I have noticed that it is harder for me to ..."
trnayon
"Michaelchondria, this is a very informative blog post. I have heard that tea ..."
trnayon
"Great blog post! As a sugar lover, I usually use multiple packets of ..."
andygen
"Largeintestein this is so cool! I think it is great that there are ..."
andygen
"This is a very interesting topic Saadoplasm! I believe that Amazon should take ..."
YusRNA
"Thank you so much for writing this article! It definitely brings up a ..."
andygen
"Wow this is so interesting Michaelchondria! An interesting idea for you to research ..."
Ethanol
"It is super neat that something as simple as habitually drinking tea can ..."
andygen
"Wow! This is extremely interesting how we might be able to eliminate deafness ..."
Ethanol
"This topic is awesome! With the excellent work of these scientists genetically predisposed ..."
Ethanol
"LOL! I was hooked by the first line. It is incredible to think ..."
actrevationenergy
"This is so cool. The possibilities for helping the environment and humanity are ..."
tsiamine
"This is a very interesting post @rivisome!!! It is very interesting to explore ..."
actrevationenergy
"I know that dead organisms are necessary for the ecosystem, but it is ..."
Ethanol
"Incredible! My two favorite things: frogs and robots! This is certainly a new ..."
actrevationenergy
"Amazing post! I found it fascinating how tea apparently lowers the risk of ..."
kangyotype
"This was very cool because I always thought that there was only one ..."
kangyotype
"I found this post to be very interesting and applicable to me because ..."
Ethanol
"Such an awesome article! We often think of the negative impacts humans have ..."
michaelchondria
"This article appealed to me because I feel like my memory is different ..."
michaelchondria
"This article interested me because it really shows how advanced our recent technology ..."
michaelchondria
"Great article! I never knew that air pollution could be linked to an ..."
michaelchondria
"This was an interesting read because I have always wondered if one could ..."
tayega
"This article is very important melaria. This brings me to the generally recent ..."
liambilicalcord
"Awesome post! Not sure how credible of a source it is, but I ..."
branchiolon
"This was a fascinating topic Alleele! Your discussion of the study involving the ..."
michaelchondria
"This article really impacted me as a huge fan of sharks in general, ..."
tytybox
"My bad totally forgot the link https://futurism.com/crispr-genetic-engineering-change-world "
tytybox
"I had no idea that biohacking was even a thing, thanks. This is ..."
trnayon
"Tsiamine, this is a very interesting topic to consider. It is very cool ..."
tytybox
"This is a really interesting moral question, and the movie gattaca we just ..."
tytybox
"It's really interesting to think about the circle of life and how animals ..."
tytybox
"This is really dope, great title by the way, totally the reason I ..."
trnayon
"This is a very interesting blog post, Liambilicalcord, and I relate to it ..."
tytybox
"This is a great post. I like how you decided to focus ..."
jednetic
"After reading this I definitely wish I could do this! An interesting article ..."
jednetic
"Fine work here Largeintestein. Here's an article debating a different sweetner–Monk Fruit– to ..."
jednetic
"Great Work Ethansol!! I found a study that details the molecular pathways the ..."
liambilicalcord
"Awesome article! Being half Irish we have tea pumping through our veins at ..."
jednetic
"That's really cool! I also just read an article about how coffee contributes ..."
jednetic
"While reading the title I also go scared as a dog owner that ..."
melaria
"Trnayon, what an interesting and relevant post! I love the connection between science ..."
tsiamine
"Thank you @branchiolon for writing this article. It was interesting to read about ..."
tsiamine
"This is a very interesting article @alleele! It was definitely amazing to read ..."
melaria
"Alleele, what an interesting study about how the time of day can affect ..."
branchiolon
"Very intriguing article! I didn't know that the friction and stress on the ..."
tsiamine
"This is very interesting @glovcose! It was interesting to read about how dogs ..."
melaria
"Maggiechondria, what an interesting post! I was shocked to find out that pollution ..."
Bronchiolon
"Job well done! I loved how your article explored the advantages of both ..."
YusRNA
"@Ethansol This is a really interesting article, that definitely speaks to a commonly ..."
melaria
"DEVOXYRIBONUCLEICACID , your blog post is just another example of how our actions ..."
metalibolism
"Great article! I think this is such an important issue. Another interesting part ..."
YusRNA
"@Liambilicalcord This is an intriguing article! I have always been very skeptical of ..."
metalibolism
"This is so interesting. Another positive for this gene therapy is that the ..."
melaria
"What a great article TRNAyon! I agree with you, and ionizingjadeation, animal carcasses ..."
metalibolism
"This is very interesting. Although there are issues with giving false or misleading ..."
tayega
"This is a very interesting as taking animal carcass removal taken into the ..."
tayega
"The editing of babies is a very slippery slope. It can help in ..."
andygen
"This is very interesting! I did not realize the importance carcasses have on ..."
@YusRNA
"@Tayega, this is a fascinating article! It’s really crazy how the changing of ..."
metalibolism
"This is so interesting. It seems that dogs are more aware than we ..."
kylsquared
"Hi Tsiamine! Thank you for this intriguing article, I had no idea biohacking ..."
kylsquared
"Hey Jessophagus! As a skincare fanatic, I really enjoyed your article! I find ..."
kangyotype
"Although using scorpion venom to fight against staph and TB, I agree with ..."
kylsquared
"Hey Ionizingjadeation! As a self-proclaimed skin care addict, I find your article fascinating, ..."
kangyotype
"Very intriguing article, michaelchondria. The thought of eating processed foods without having to ..."
largeintestein
"This article was really fascinating! I never actually knew why skin becomes wrinkled ..."
metalibolism
"This article was very interesting! I think this is an issue that everyone ..."
kangyotype
"Wow I was shocked to see how a fungus can completely take over ..."
largeintestein
"This entire study is mind boggling to say the least. Human innovation has ..."
kylsquared
"Hey Maggiechondria 🙂 Super unique article choice! I find it fascinating that although ..."
Kyla
"Hey Maggiechondria :) Super unique article choice! I find it fascinating that although ..."
largeintestein
"I feel it is so often that we only think about the atmosphere ..."
Branchiolon
"Great article! The discover of the two patterns of DNA damage caused by ..."
largeintestein
"It's truly startling to think that humans have caused so much damage to ..."
largeintestein
"I really enjoyed reading this article because it was very relatable to my ..."
Branchiolon
"Great job Andygen! The fact that most of these ancestry services use algorithms ..."
Brandon
"Great job Andygen! The fact that most of these ancestry services use algorithms ..."
devoxyribonucleicacid
"It's amazing to see how scientists and researches are looking for interesting ways ..."
Bacterina
"In an age where we are able to see the harmful environmental effects ..."
Bacterina
"Thank you Aleele for writing about this topic! I find it quite interesting ..."
Bacterina
"It is interesting to hear all the positive factors of Stevia since my ..."
Bacterina
"Sorry, Maggiecondria link didn't go through :) https://www.niehs.nih.gov/research/programs/geh/climatechange/health_impacts/neurological_diseases/index.cfm "
Bacterina
"Maggiecondria! I never knew there was a correlation between schizophrenia and air pollution. ..."
tayega
"This is very interesting dannimal. The corona virus has caused so much panic ..."
Bacterina
"While looking through the articles written by our fellow classmates, as soon as ..."
alleele
"Interesting article! I wonder about other factors, such as the temperature of the ..."
jacuole
"Tsiamine, thank you for writing about this topic, because I've never heard of ..."
abbyogenesis
"This is so cool! More and more we see in the news how ..."
jacuole
"Sharks have been around since the dinosaurs, so it's so crazy to me ..."
abbyogenesis
"As we get older zombies like Santa and the tooth fairy are among ..."
abbyogenesis
"Wow this post is so interesting! It truly shows how advance we are ..."
jacuole
"Saadoplasm, it was refreshing to read this article, because oftentimes the threat of ..."
abbyogenesis
"As a fellow tea drinker this blog post is amazing! I am so ..."
ionizingjadeation
"This is so fascinating, tytybox! These robot frogs could be the first step ..."
abbyogenesis
"I always knew dead animals were beneficial to the environment but I ..."
ionizingjadeation
"I completely agree with you, trnayon. Animal carcasses should be allowed to be ..."
ionizingjadeation
"What an interesting blog post, kangyotype! It is so fascinating to see how ..."
ionizingjadeation
"Great blog post, michaelchondria! I have actually heard a lot about the benefits ..."
Johnomer
"I was interested in reading this article because there are so many products ..."
Johnomer
"I liked reading about this article because I got to disprove my parents. ..."
Johnomer
"I enjoyed reading this article because I find the concept of stopping aging ..."
Johnomer
"I found this article very interesting and I think you did a great ..."
jervissystem
"On the concept of CRISPR, there is a question about how it will ..."
jervissystem
"This article shows an effective symbiotic relationship. Both the human and the gut ..."
Johnomer
"I found this article very interesting because I never thought drinking tea could ..."
ionizingjadeation
"Great blog post, liambilicalcord! It's very comforting to know that the radiation from ..."
jervissystem
"This article truly shows how important mucus is in human bodies and how ..."
foodvacuolola
"Great post Rivisome! So fascinating that scientists have the ability to give us ..."
foodvacuolola
"The title says it all and it definitely catches my eye! I immediately ..."
foodvacuolola
"I saw this blog post and immediately had to read because I love ..."
foodvacuolola
"Great blog, it is crazy to think and put into perspective how the ..."
ionizingjadeation
"How interesting, nucleahtide! He Jiankui's actions regarding genetically modifying these twin girls' embryos ..."
foodvacuolola
"I find this really interesting because we can use the gut microbiome to ..."
jacuole
"Sharks have been around since the age of the dinosaurs, so it's sad ..."
devoxyribonucleicacid
"This article is really interesting, Tytybox. It's wonderful to see how technology has ..."
jackuole
"I found this really interesting Saadoplasm, because the idea of one realistic change ..."
nukellyicacid
"The effects of climate change and ways to combat it are by far ..."
nukellyicacid
"Great article! I’m glad that there is a potential treatment for sickle cell ..."
nukellyicacid
"The use of CRISPR to edit genes in the DNA sequence in order ..."
nukellyicacid
"Great job! I’ve never known that in order to maintain long term memories ..."
nukellyicacid
"I think it’s really interesting how research is being done to potentially extend ..."
devoxyribonucleicacid
"Really interesting article, tayega. I also do believe that Jianku's actions were very ..."
Handroanthus
"This is a very well written blog. I like how you did not ..."
devoxyribonucleicacid
"Really interesting article, dannimal. I think you did a really great job at ..."
helenogenous
"Thanks for sharing @GLOVCOSE! It was interesting to learn that humans and dogs ..."
helenogenous
"What an eye-opening article @KYLSQUARED ! I think a lot of people could ..."
helenogenous
"Wow @TRNAYON, your blogpost really brought up some interesting ideas and points, especially ..."
helenogenous
"Great article @YUSRNA! I loved learning how the same protein was involved in ..."
helenogenous
"Great article @YAMAGUTIPLECTOGNATHOTREMA! Interesting observations about how people only tend to remember their ..."
maggiechondria
"Hi Ethansol, your article was fascinating! I find it so interesting that Sestrin ..."
maggiechondria
"Tytybox, this is extremely interesting and intriguing. I find it amazing that a ..."
devoxyribonucleicacid
"I believe this topic is very interesting, yet extremely controversial in some cases. ..."
Charlo Englaeic-acid
"Wow! great article, possibly the most well-written I have read so far. ..."
EvoluChen
"I like how this post not only answered the question, but also went ..."
Widgeon
"Very interesting article Andygen. I completely agree that these tests are not completely ..."
rivard
"This is very interesting! I this is an interesting idea of building muscle ..."
a
"I really liked the information and research you provided in your article. I ..."
Anamino Maronomer
"Now that I know my microwave won't kill me, I can still enjoy ..."
charlaphroditic Englernation
"I enjoyed the article, but I found the data in the second paragraph ..."
rivard
"This article is very interesting. It is great to see how technology is ..."
Broteria
"This blog is very different and seems new and exciting. The technology ..."
Joule
"I found this article very interesting. I love dogs a lot and to ..."
DNAiel
"This post is very interesting, and I was hooked from the heading! It ..."
Widgeon
"I liked your article, Ethansol. Sestrin would be a great idea and drug ..."
Quadruplex DNA
"I think this article is very well written and shows how we humans ..."
Alizard Wrat
"This article is extremely intriguing! It's interesting to see how a drink ..."
EvoluChen
"I liked how this post has a very unique topic and how it ..."
Charmunnity Englandiffusion
"Very interesting article! I thought it was cool that the animal is ..."
jacuole
"TYTYBOX, I can't lie, this freaks me out. I understand their practical use ..."
jacuole
"Michaelchondia, thank you for telling us about this research! I never would ..."
maggiechondria
"Hi CELLILLYMEMBRANE! I think your research was extremely fascinating. I would have never ..."
jervissystem
"That is very interesting how the animals, contrary to what might typically happen, ..."
jervissystem
"This is a truly interesting study in how something as small as a ..."
cellillymembrane
"My parents also always told me not to stand in front of a ..."
cellillymembrane
"I think that this article has a lot of eye opening facts. It ..."
cellillymembrane
"This article is very interesting! I didn’t know that Setiva is so expensive ..."
cellillymembrane
"I think it’s very interesting how just the time of day can affect ..."
maggiechondria
"Personally, I never really knew the true causes of celiac disease. It is ..."
maggiechondria
"Michael, your research on how habitually drinking tea contribute to living a longer, ..."
cellillymembrane
"I never realized how important animal carcasses are to various ecosystems. When I ..."
nucleahtide
"Largeintestein, there are clearly several benefits to using the stevia leaf as a ..."
nucleahtide
"Hi Maggiechondria! I think it is very interesting how seemingly unrelated factors can ..."
nucleahtide
"Very interesting article, Ethansol! Though sestrin may be able to replicate the physical ..."
nucleahtide
"Doing further research on microwaves, microwave light is non-ionizing radiation, meaning it does ..."
nucleahtide
"Wow, michaelchondria! I was reading an article about the ingredients of tea and ..."
angtigen
"I enjoyed your article cellillymembrane. I agree it's interesting to see how samples ..."
angtigen
"I enjoyed your article kylsquared. I didn’t realize efforts were being made to ..."
angtigen
"I enjoyed your article melaria. Connecting photosynthesis to our climate is very interesting. ..."
angtigen
"I enjoyed your article Kyla. I didn't realize efforts were being made to ..."
brianaryfission
"With the increasingly alarming spread of the coronavirus, the topic of vaccinations also ..."
brianaryfission
"While the inaccuracies of ancestry.com are evident, the use of DNA in police ..."
brianaryfission
"It's super interesting to see the largely useful nature of saliva in terms ..."
brianaryfission
"After searching up Sestrin, I read something really interesting from the Michigan Daily: ..."
brianaryfission
"Following up on your analysis of the increasing concern around schizophrenia, I found ..."
jessophagus
"I have been thinking about the impacts of commercial delivery recently, having a ..."
jessophagus
"I completely agree with Bacterina’s stance. It is fortunate that sharks have found ..."
jessophagus
"This article hits close to home because my younger sister suffers from celiac ..."
jessophagus
"I agree with Andygen in that ancestry tests are less accurate than they ..."
jessophagus
"I’ve definitely had a similar experience to Liambilicalcord and many, with an underlying ..."
angtigen
"I really enjoyed your article abbyogenesis. From the title of your article to ..."
angtigen
"Your article is really interesting branchiolon. It's cool to see how these worms ..."
alleele
"It is so upsetting that human consumption is leading to increased acidity in ..."
alleele
"I found this study (http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0058871) which talks about how Stevia can potentially reduce ..."
alleele
"Glad to hear microwaves are safe, so I can keep enjoying my pizza ..."
alleele
"This is really cool! It is exciting to see technology develop, even if ..."
jouleia
"Great article! I think most likely one of the main reasons that someone ..."
jouleia
"I loved this article and found that it illuminated many new aspects regarding ..."
jouleia
"While I think this article is super cool and helpful, I think it's ..."
jouleia
"I have also been told growing up that the microwave is bad, in ..."
jouleia
"This is super interesting! I know you mentioned that green tea is the ..."
Yusra Azaz
"@MICHAELCHONDRIA, thank you so much for posting this article! It is truly thought ..."
meangela
"Nice article Brian. I didn't realize there was an overpopulation of kangaroos in ..."
maggiechondria
"good work! "
mikeochondria
"I would just like to extend my previous comment and add a link ..."
mikeochondria
"I think this is definitely a revolutionary discovery. The fact that they ..."
chromison
"Nice article YUROGENITAL, the effects of climate change on different species of animals ..."
chromison
"Great article PUNNETSTEPHENS, the research being done on antibiotic-resistant bacteria is both incredibly ..."
punnetstephens
"Yawning is as much Biology as Psychology. The saying does go "monkey see, ..."
chromison
"Interesting article EKAULI, this is one of the many pressing and important environmental ..."
punnetstephens
"A little funny how the same classification of DNA is associated with both ..."
chromison
"Very interesting Kelsium, the analysis of DNA in greater detail truly represents the ..."
chromison
"Fascinating article Smoothxander. Studying the links between radiation and cancer is something that ..."
evodrewtion
"Great job, SHAROTHYMINE! I love science, but why does it have to ruin ..."
punnetstephens
"A Vaccine for a disease which at one point infected about 5,000 people ..."
ekauli
"I always hear about stem cells in the news and in new research, ..."
evodrewtion
"Very interesting! Although I am a man, after reading this article I ran ..."
ekauli
"This topic is especially interesting to me, like those above, because of my ..."
ekauli
"That's a really an interesting post. I don't think when people get tattoos, ..."
evodrewtion
"Wow IFEMURBONE!! This was fascinating to read. After reading this I was curious ..."
punnetstephens
"With the chart, the reason O blood is able to give blood to ..."
ekauli
"I've done multiple projects in biology on invasive species, and I think they ..."
ekauli
"This is a really interesting topic, and maybe a potential answer to dealing ..."
celliswallier
"Hey Ekauli, I found a very recent article that you may find interesting. It ..."
celliswallier
"Hey Mattabolism, So... This happened. Ok, well not quite. Just a couple days ago ..."
celliswallier
"Hi Yurogential, There's also a additional risk to many humans caused by the shrinking ..."
celliswallier
"Hey Sgagliotide, While this may be a weird statement, this seems like a very ..."
celliswallier
"Hey Chromison This post is important. My family goes camping a lot and a ..."
punnetstephens
"@Matosis the facts that scientists were able to get this two-part action from ..."
AllergyEasy
"Those who suffer from nut allergies will learn many things from this article. ..."
gabdomen
"There are so many different findings on what causes alzheimer's. However this seems ..."
evansymes
"Interesting post CAROLENZYMES, and nice username (one of has has to go home ..."
evansymes
"This is a very interesting and well written post on a subject that ..."
evansymes
"Ok. Wow SARAHTONIN, I didn't know you felt this way. This is hurtful. ..."
evansymes
"Cool article SEJEOLOGY, very informative and interesting. One point I noticed that you ..."
evansymes
"very interesting article GOLDGI. Your title was definitely successful in drawing me ..."
Ramesh Chandra
"Why do evergreen trees have thick and shiny leaves....... "
hutcherozygous
"I found an article that says that a roundworm, similar to the one ..."
qtytree
"I found another website that talks about this theory on if animals are ..."
oxergin
"I think that yawning is a very interesting unknown in the world of ..."
oxergin
"Tourism plays a huge role in threatening the Great Barrier Reef. In fact, ..."
oxergin
"Like you mentioned it is more important to live healthier years rather than ..."
oxergin
"Maybe this chemical balance of dopamine is extended to more than just bees. ..."
oxergin
"I think that this topic is very interesting! Research that leads to more ..."
evansymes
"Very interesting and very well written phospholipidbellayer. I've always heard that the primary ..."
evansymes
"Everyone knows that seeing other people yawning makes you more likely to feel ..."
evansymes
"forgot the link to the second article http://www.space.com/17828-mars-weather-curiosity-rover-discovery.html "
evansymes
"When I read this I can't help but feel like its ridiculous for ..."
evansymes
"My first reaction is that the Dinosaur namers seem to have gotten really ..."
evansymes
"In the end of your first paragraph you wrote that mole rats are ..."
hutcherozygous
"There was also a study that found the bees to experience anxiety . ..."
hutcherozygous
"You mentioned at the end that the dust storms could be signs that ..."
hutcherozygous
"Not being able to feel pain is definitely not always an advantage, but ..."
gabdomen
"This was very interesting to me, cause I get migraines a lot and ..."
hutcherozygous
"Turns out that in addition to avoiding stress, there is a new procedure ..."
Vicky
"I am sorry but I think the research design is problematic. What's the ..."
organelle
"This article is super interesting! It really makes me think of all of ..."
Leukemia
"Biospearb, great article on such a relevant topic! I, for one, am immensely ..."
Leukemia
"Interesting how one drug intended for one part of the body can affect ..."
Leukemia
"Nice article Jackuole! I found an article that discussed a similar topic, surrounding ..."
Leukemia
"Benadryl, great article! You define well the dangers and recent developments on the ..."
Leukemia
"This is a very concerning situation that is adversely affecting a large number ..."
jdna
"Wow, this can really lead to amazing breakthroughs. We are already on ..."
jdna
"Imagine a person similar to the likes of Captain America walking on planet ..."
jdna
"Gross, but innovative and informational. Never thought donating fecal matter would ever ..."
jdna
"Cool Article. Its once again really interesting to see how much microbiomes ..."
jdna
"I always knew Phys Ed class was more than it seemed! Microbiomes ..."
fineflagellum
"This is a very interesting piece, especially since so many people are interested ..."
agman
"Wow. Lukemia this has the potential to change history. While further studying this ..."
agman
"Thank you for this article!!! The scientific world has really been changed by ..."
agman
"Benadryl, WOW! It's hard to believe that anyone smokes cigarettes! Thank you for ..."
agman
"Sheasexual thank you for this incredible article!!! As a frequent coffee drinker I ..."
agman
"Excellent article Jackuole! it is so interesting to read about the functions of ..."
Caroline
"We eat what we are. I have read an article from other site. ..."
jdna
"Mars is always interesting topic of study! I always thought it to ..."
jdna
"Another great article! Elephants are quite interesting mammals. Their trunks are unique ..."
jdna
"Awesome article Sabraina, but it's upsetting such harmful and cute monkeys have to ..."
jdna
"Interesting and relevant article peptidechiangs, as the over consumption of sugar plagues the ..."
jdna
"Wow! Its crazy to believe there are so many undiscovered species on Earth! ..."
joules
"Cool article! Did you know that the Oenococcus oeni bacteria contributes to not ..."
joules
"Like you mentioned about the Yellow dye, Kraft foods is removing their yellow ..."
joules
"I used to have a penicillin allergy too! After further testing and years ..."
joules
"This is so interesting endotheleeum! After further research, I learned that INMI's can ..."
joules
"Great article Sabraina!! I love elephants and after researching more about their trunks ..."
agman
"Thanks for the great article Endotheleeum! I constantly get songs caught in my ..."
agman
"This is a great article Peptidechiangs! Thank you! I never knew that memory ..."
agman
"Izerstellar great article! I love learning about our solar system. I found a ..."
agman
"Excellent article Vissictomy! I always appreciate minds invested in biology. Also thank you ..."
agman
"Fascinating article sabraina! I particularly enjoyed the discussion of what can be defined ..."
jackuole
"Great article Biodeversity! Did you know that the existence of the Homo Naledi ..."
jackuole
"Always thrilled to hear about the discovery of a new species Vissictomy! Despite ..."
jackuole
"Very informative Izerstellar! New studies: http://financialspots.com/2015/11/08/martian-atmosphere-was-stripped-by-solar-wind-nasa/ show that at one point Mars may have been ..."
jackuole
"Great article Sabraina! When I was reading your article, I could not help ..."
jackuole
"Great article Peptidechiangs! The downsides of an over dependence on sugar truly are ..."
peptidechiangs
"Such a cool and thought provoking topic! Great article Benadryl! I also read ..."
peptidechiangs
"Super interesting article marsupialniche! It is amazing what technology can do these days ..."
Antibody
"I never thought the breath of fresh air could be helpful in asthmatics. ..."
sheasexual
"Very interesting article! I read about an article that talked about how actual ..."
sabraina
"Wow, what an informative article. Fineflagellum, thank you for those statistics as well; ..."
fineflagellum
"This was a very interesting article, thank you Zerillium. It has been interesting ..."
Nicheloss
"Nice article! When I read more on the crystalline lens, I found a ..."
herarst
"This is so cool. I didn't know much about the Komodo dragon before ..."
herarst
"Good article. When you play football there's always going to be a chance ..."
herarst
"This is really interesting mitokahndria. I didn't really know about the Head Start ..."
kysquared
"Very interesting and unfortunate, sgagliocytosis. I wonder if human intervention can save the ..."
kysquared
"Interesting article, andybody! I wonder if this same process could work for getting ..."
pintocytosis
"Interesting article vivzett! Its fascinating and somewhat concerning that such serious diseases can ..."
pintocytosis
"Interesting article gherloniapparatus! It is so interesting and worrisome that the companies that ..."
camouflage
"This is such a great article. It really makes you think about how ..."
camouflage
"Wow, izotope, this is a very interesting article! I have always wondered myself ..."
gigabytes
"This article touches upon a critical subject. It seems as if the nation ..."
gigabytes
"This is a very important and interesting topic. By messing with our food ..."
gergory
"Hey! I love this article. It is really cool to me how there is ..."
blevans1
"I have always heard that video games are so bad for your brain ..."
blevans1
"This is a really interesting topic. The gluten- free trend is so ..."
blevans1
"This is a really cool article. Optical illusions have always seemed almost ..."
blevans1
"This is a really interesting article. It just shows another reason why ..."
blevans1
"It's amazing that people are making these type of innovations. The amount ..."
blevans1
"This is really interesting. It's surprising to see the widespread effects of ..."
sgagocytosis
"This is a scary and interesting article, Menstruation! I just read something that ..."
sgagocytosis
"This is an interesting article and new view on video games!! I've always ..."
gherloniapparatus
"Great article, kation! This is something that we never really come across - ..."
gherloniapparatus
"Wow, this is such an interesting article! We always talk and hear about ..."
andybody
"That's very interesting. I wonder if the experiment would have the same ..."
andybody
"Very well done. It's interesting to read about the real affects of global ..."
izotope
"Very cool! Being in school, it is interesting to see how we can ..."
izotope
"What an interesting article! I never thought of how increased water vapor could ..."
fishinthesie
"My psychology class recently looked at this image. My teacher had the class ..."
fishinthesie
"This is really interesting pintocytosis! I think people often wonder if eating healthy ..."
whitebloodcell
"Great article! The potentials of this invention are vast. A similar article describes ..."
whitebloodcell
"Very interesting article! I know that lightning causes many wildfires in the United ..."
Lord of the blood cells
"Really interesting stuff! As I was reading, I got more and more anxious ..."
Lord of the blood cells
"Great topic mitokhandria! I also am very alert towards what is in the ..."
simbiotic
"Great article rheaction! Did you also know that coffee boosts your metabolism! That ..."
simbiotic
"Great article rheaction! Did you also know that coffee boosts your metabolism! That ..."
pintocytosis
"Interesting article kation! After hearing time and time again that video games rot ..."
pintocytosis
"Nice article mjb96! It is good news that research is being done to ..."
simbiotic
"Great article Sgagocytosis! I actually am also a vegetarian, and have been considering ..."
fishinthesie
"I definitely agree that medication isn't the only option and that there are ..."
simbiotic
"What a great article Camouflage! To elaborate on the idea of depression and ..."
fishinthesie
"This is so surprising! I've been following a vegetarian diet for about 7 ..."
gherloniapparatus
"Here is a link to the article about the lionfish: http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/07/080717164319.htm "
gigabytes
"You are touching upon a very important issue. What will our world look ..."
gigabytes
"As a regular coffee drinker, this article was very interesting. I always make ..."
izotope
"Great article rheaction! Granted I drink a lot of coffee myself it is ..."
izotope
"What an interesting article camouflage! I always assume depression comes from chemical imbalances ..."
whitebloodcell
"Great article izotope! I definitely agree that medication is not the only answer ..."
whitebloodcell
"Great article rheaction! It seems like coffee provides so many health benefits. I ..."
rackolam
"Looks like I can use this as my reason to drink coffee now. ..."
rackolam
"Interesting article Gigabytes. It never occurred to me that taking notes may actually ..."
nicheloss
"Nice article-all the research on coffee's health benefits is exciting. I did some ..."
nicheloss
"This is great news for coffee drinkers! I read some more about coffee's ..."
nyrsoccer
"Very cool! In my mind there is most likely other intelligent life, possibly ..."
nyrsoccer
"Shocking considering not too long ago scientists came out with studies that writing ..."
sgagocytosis
"Interesting article, Gherloniapparatus! It's always fascinating to see articles that can look further ..."
sgagocytosis
"Sorry, Gigabytes***! "
sgagocytosis
"Interesting article, Gigbytes! I've always thought that physically writing down information with a ..."
balsamic
"Great article Vivian! Ebola's complexity, contagiousness and fatality rate make it a very ..."
herarst
"I've never made the connection of heating up food and causing denaturation in ..."
herarst
"Very cool and interesting article. It's always fascinating when a new planetary discovery ..."
mitokahndria
"love the article! I love exercise and I try to do at least ..."
mitokahndria
"Great article Julia!! I still find it so interesting how someone could simply ..."
camouflage
"This post only encouraged me to exercise even more. I really had not ..."
camouflage
"This is super interesting in that I had no idea there were fish ..."
gergory
"Good article! I am also very interested in the potential presence of extra-terrestrial ..."
gherloniapparatus
"Such an interesting article. It's amazing, yet so scary, to realize that there ..."
gergory
"Nice article, Lord of Blood Cells! I really enjoyed reading about the benefits ..."
gherloniapparatus
"Great article, Nicheloss! This topic is so interesting especially because, like you recognized, ..."
andybody
"Oh and here is the article where I read about this:http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/releases/285077.php "
andybody
"Researches from the Harvard Stem Cell Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital, and Boston Children's ..."
andybody
"Yes struan, great post. It's disheartening to read about how so many ..."
Lord of the blood cells
"Great post struan. It is crazy to think about how vast and rich ..."
pintocytosis
"Great article! I really enjoyed the questions you posed to the reader, and ..."
pintocytosis
"Great article! I have heard something similar to this article before and it ..."
sgagocytosis
"This is a very interesting article Gergory! I try to avoid drinking any ..."
sgagocytosis
"Very interesting article, Fishinthesie! I always think of reptiles being more closely related ..."
fishinthesie
"This is really interesting. There's a lot of debate out there about the ..."
mitokahndria
"Awesome article Samer! Hearing about Ebola on the news and the severity of ..."
mitokahndria
"This article is so interesting and I feel that it is extremely relevant ..."
whitebloodcell
"Great article kation. I read an article on the assisted migration of whitebark ..."
whitebloodcell
"Very interesting article gergory. People have always said that artificial sweeteners, especially the ..."
Lord J-blood cells
"Greg, great post. Reflects how artificial sugars can really affect our health. The ..."
simbiotic
"Great article Kation! I never knew there was even such a thing like ..."
simbiotic
"Great article choice! Did you know that artificial sweeteners are widely accused of ..."
nicheloss
"It's so interesting how even with all the frightening overdose statics, packaging ..."
nicheloss
"This is definitely an alarming side effect for using a supposed "healthy" substitute ..."
herarst
"Good article Samer. Not surprised to see scientist taking action against Ebola after ..."
herarst
"The article is very interesting. A lot of these artificial sweeteners claim to ..."
nyrsoccer
"No one can be sure how language first came about in humans, but ..."
nyrsoccer
"I do not think humans should assist nature. Nature has sustained itself throughout ..."
covalentbond
""Each generation takes the earth as trustees." -J. Sterling Morton Does natural selection still ..."
covalentbond
"Really great article! I did mine on the microbiome so I might have ..."
camouflage
"First of all, real punny with that title, definitely caught my eye. Secondly, ..."
camouflage
"This article is super thought provoking-- I have never thought about the "child ..."
gigabytes
"This is a very interesting article. It ties into both environmental and moral ..."
fishinthesie
"I think that the idea of assisted migration has a good intention behind ..."
izotope
"What a great article Gergory! Artificial sugars have always been interesting to me. ..."
izotope
"Oh wow gherloniapparatus! What an interesting article! I never realized the risk children ..."
gigabytes
"Great article rheaction! I recently read an article that provided a commentary on ..."
gergory
"Very interesting article Samer. I am very interested in the potential treatments of ..."
gherloniapparatus
"This article is so informative! It's so scary to see the spread of ..."
gherloniapparatus
"This article is really interesting! It's surprising to read about sugar substitutes being ..."
gergory
"Hey Kyle, great article! Horrible name though. I have a few comments on ..."
kysquared
"Very interesting article! What about different types of artificial sweeteners? I read about one ..."
kysquared
"Very interesting article, Samer :-) I'm very curious as to how worried I should ..."
andybody
"Very interesting article Kyle ;-) I've always had a few questions about language ..."
andybody
"Very interesting article Samer. It's amazing that Ebola has managed to spread unchecked ..."
cjobios
"What a strange way to go! I recently learned that Pacific Salmon also ..."
rmelman
"That is so cool! Animals are so intelligent. It is really interesting that ..."
rmelman
"This is awesome! I can't wait to bring my phone into various dangerous ..."
danasaurus
"Great article! It is interesting that we probably experienced or will experience this ..."
danasaurus
"I can't blame the lizards for being more tame on nice islands! I ..."
segolene
"Neat article! This is very interesting to know as a dog owner myself. ..."
segolene
"Neat article! This is very interesting to know as a dog owner myself. ..."
segolene
"Very good article! The development of the brain is surely a crucial part ..."
rmelman
"Wow! It is always great to hear new information on the immune system, ..."
rmelman
"Interesting, I always wondered why us teens act out against authority! When do ..."
biolivcious
"Great post! I find this interesting because I wonder if the frontal lobe ..."
orsbio
"This is so cool! I've always wondered about how a wagging tails relates ..."
orsbio
"This is such an interesting post as it pertains to all of us! ..."
rmelman
"Cute!! It's interesting to see that dogs can communicate with their tails, rather ..."
celine2
"This is interesting to read! After a little bit of research, here is ..."
celine2
"This is really interesting! I would have never thought of a difference between ..."
cjobios
"Sorry, here is the link to the article I mentioned: http://www.cell.com/current-biology/abstract/S0960-9822%2814%2900123-7 "
cjobios
"This is really interesting! I found an article, also published by Current Biology, ..."
rubinka
"Good job em83! It's interesting how you related the more psychological findings of ..."
rubinka
"Great post termitelover! I liked how you included the process the scientists used ..."
sciencekid1
"This was an incredibly interesting read! I find it amazing how things ..."
karbonkim
"This is a great post! This study is another step toward further understanding ..."
karbonkim
"What an interesting discovery! I have seen birds fly in this "v-formation" numerous ..."
Sameer
"The above theory suggests that you will wake up at the same time ..."
katnizz
"Interesting! I had never thought about the direction of dogs' tails meaning different ..."
katnizz
"Wow this is really interesting and relatable! this got me thinking and eventually ..."
orsbio
"This is such a cool post! I've never heard of Biosforsk before nor ..."
segolene
"This article has much truth. Teenagers get their caffeine intake through many sources ..."
segolene
"Interesting read. I recently just finished a French project that focused on issues ..."
segolene
"Wow! This article brings great news for adults. Maybe this discovery could lead ..."
segolene
"Interesting article! I agree with you in that many students tend to take ..."
segolene
"Great article! I can definitely relate to this because last year I tore ..."
orsbio
"Wow cool post! Just looked up a picture of the butterfly, and it's ..."
biolabski
"While you discuss harmful effects of GMOs on human health, introducing them into ..."
biolabski
"This is certainly a controversial topic, for many studies show that the brain ..."
biolabski
"This is interesting, because most species become endangered due to human activity, rather ..."
biolabski
"That's cool news! There was another published article that discussed how having cats ..."
biolabski
"Wow, Paul Segond sounds like a really cool guy! It's impressive that he ..."
celine2
"I loved this article. It stands out to me, a person who is ..."
celine2
"This is interesting to read! We often always hear about the negative aspects ..."
katnizz
"that is such a shame! i for one love scuba-diving and by the ..."
katnizz
"interesting how you linked this article to wolfpacks. After thinking about it and ..."
katnizz
"I find this really interesting and can really appreciate all that Brown scientists ..."
katnizz
"I agree biolivcious! German's initiative toward alterative energy is incredible! Here is another ..."
katnizz
"wow! This article seems not only interesting but important to the possibilities of ..."
termitelover
"Very interesting. Perhaps if there is gene that can perform these functions in ..."
termitelover
"These finding are very interesting. I wonder what benefits other plants may have ..."
termitelover
"Good to see that knee injuries can be fully operated on now that ..."
biolivcious
"It was very interesting that the rare male effect was not present in ..."
biolivcious
"This is such a great breakthrough! I am curious, however, as to how ..."
biolivcious
"This was a very surprising topic to read about. I never before heard ..."
biolivcious
"So interesting! I wonder if this discovery could be used as "fountain of ..."
biolivcious
"Wow! What amazing discovery! I really believe this will change orthopedics. I can't ..."
cjobios
"When we sleep, our bodies need to dispose of "toxic metabolic byproducts." These ..."
cjobios
"The mortality rate of Tasmanian devils is crazy! According to http://www.nature.com/news/vaccine-hope-for-tasmanian-devil-tumour-disease-1.12576, if no ..."
karbonkim
"Wow! What an amazing achievement for Mr. Andraka and innovation for pancreatic cancer ..."
celine2
"I am surprised at how coral bleaching seems so harmless but is indeed ..."
celine2
"This article is very interesting! I am glad to see that we've progressed ..."
biolivcious
"While this new laser technology sound extremely promising, it also occurred to me ..."
biolivcious
"I am impressed the German initiative towards alternative energy. Here is an article ..."
segolene
"Wow! Great article! It was intresting to read that scientists have been able ..."
segolene
"Great article! I also wrote a summary on an article about a ..."
karbonkim
"I thought this was an interesting post. As a young person, I can ..."
pat
"Cool topic melman! I think it is interesting that scientists would try to ..."
termitelover
"As a high school student I'm constantly seeing kids with coffee to get ..."
termitelover
"Nice to see progress in one of the final frontiers we have yet ..."
termitelover
"Sharks have outdated all of the mass extinctions on this planet making them ..."
Devin
"I swear I had an intellectual growth spurt when I was 17. ..."
rubinka
"Great post! I think you explained this complicated topic very well! This is ..."
rubinka
"Great post! I find it very interesting that the discovery of a single ..."
celine2
"This article was very interesting, and it was also very interesting to see ..."
celine2
"This article is very interesting. I've done some research on this topic, and ..."
celine2
"This blog post is very interesting to me, because several of my friends ..."
biolabski
"How interesting! Reading this immediately reminded me of wolf packs. Wolves are known ..."
biolabski
"I think that this article touches on an important problem that many teenagers ..."
cjobios
"Many scientists have studied elephant behavior, and have concluded that they (they elephants) ..."
cjobios
"I meant to add that Tylenol can lead to liver damage, while NSAIDs ..."
cjobios
"I think that it's really important that the dangers of Tylenol (as well ..."
rmelman
"I found an article that is about different types of noise-canceling and noise ..."
rmelman
"This article is fascinating! I found an article that discusses how nature can ..."
Thans
"This information is fascinating. It is really cool and, yet also scary, to ..."
Thans
"I too enjoyed this post. Upon reading this I was like, "huh isnt ..."
segolene
"Great article! It was interesting to read that this butterfly's wings can lead ..."
segolene
"HIV is unfortunately a disease that is spreading rapidly and affecting millions of ..."
danasaurus
"This is a very cool article! It is crazy to think that the ..."
danasaurus
"This is a very interesting post! It is amazing to think that producing ..."
rubinka
"I thought this post was very interesting! I liked the discussion of why ..."
rubinka
"I was definitely interested by your discussion of naturally inspired technologies- and I ..."
palindromeprincess
"The image that you have attached with this article is very powerful and ..."
biolivcious
"Personally I feel that the positives outweigh the negatives when it come to ..."
palindromeprincess
"This article caught my attention right away because I am currently reading "The ..."
celine2
"Obesity is definitely a major problem in America. Another article has shown that ..."
celine2
"It is very interesting to try answering the question of why we love ..."
karbonkim
"This is a really cool post! I would never have thought about the ..."
karbonkim
"I really enjoyed this post. I found it interesting to learn about the ..."
biolabski
"I think that this is a very important article because the failure of ..."
biolabski
"I think it's really cool that scientists were able to link an everyday ..."
R M Aggarwal
"I do sometimes, and in fact generally wake up in the morning, before ..."
ploop
"good source of information "
thephilosopher
"It is interesting that telomeres are correlated with an increased chance of survival ..."
thephilosopher
"Unlike viruses like the common cold, HIV can hide itself in our cells ..."
sciencegirl025
"Great synopsis! GATTACA was rated one of the top science movies among others. ..."
sciencegirl025
"Cool article! It definitely makes sense that it would improve the cognitive abilities ..."
jk1234
"This is a very dangerous disease hitting the tasmanian devil population. Luckily is ..."
jk1234
"This is an incredible find. It's also incredible how much progress we have ..."
leahna
"My mom and I (she's a dietician) talk a lot about the pros ..."
leahna
"http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/traits/telomeres/ This is fascinating! According to the article above, scientists are learning to apply ..."
sayrest4
"It is really interesting that Tasmanian Devils have lost the ability to recognize ..."
sayrest4
"This is great news! Currently we only have a way to slow down ..."
biorob
"Great post! I was looking for an article to write a post about ..."
biorob
"This is a great post and a huge breakthrough in the world! We ..."
evolucious
"For some reason, I did not know that cancer could affect animals other ..."
evolucious
"Apparently, video games also can help improve eyesight by "teaching the brain to ..."
evolucious
"I agree with the previous two commenters; GM foods have been shown to ..."
hannahbanana
"Wow! What a breakthrough! This is very cool!! I hope this is something ..."
hannahbanana
"This is a very interesting post. I like how the author pointed out ..."
hannahbanana
"This is very interesting article. Recently, I was reading this article:http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/11/121101121604.htm. Your post ..."
saysquad
"This is a great article rawgdog! I find this subject to be very ..."
henroids
"While certain video games might help with concentration, they must be played with ..."
saysquad
"This is a great article! I believe the correct grammar would be: read ..."
troybolton
"Very cool! It is interesting to see how video games can help elderly ..."
thephilosopher
"Good article. I think that the inaccuracies in Osmosis Jones are excusable given ..."
thephilosopher
"Interesting article. There has been a bit of a change of attitude towards ..."
troybolton
"Very cool subject! I personally think that Genetically Modified Foods are an interesting ..."
troybolton
"It is a shame how many people in this world have contracted AIDS. ..."
troybolton
"This is really cool! I guess I am going to use this as ..."
troybolton
"Nice article! This is an interesting alternative to the typical liposuction or gastric ..."
henroids
"WE DID IT! The first baby ever has been cured of HIV! Recently ..."
henroids
"When I got out of the shower today my fingers were wrinkled and ..."
jk1234
"Great post bg95! Cocaine addiction is certainly a scary thing and the frontal ..."
ilikebioha
"I believe this study to hold a lot of truth. In my ..."
henroids
""I sometimes think I can do crystal meth, but then I think, hmmm, ..."
jk1234
"Wow! I never thought that there would be so many down sides to ..."
ilikebioha
"Henroid I think what you said is interesting and i wondered if SM ..."
dwil
"When I was a kid, I never was able to go to sleep ..."
dwil
"I think it is very interesting how almost all living things are linked ..."
sayrest4
"I wonder how this disorder affects feelings such as phobias. Since phobias are ..."
sayrest4
"Great article! Apparently some people believe that it will go away if they ..."
inewitt
"Very interesting. I found this article about one of the CNVs that lead ..."
inewitt
"Very interesting, I always like to see the hidden benefits, and also weaknesses ..."
leahna
"http://www.nrdc.org/breastmilk/benefits.asp Whether or not it's certified or informal milk, there are many benefits of ..."
leahna
"http://www.standard.net/stories/2012/02/06/many-benefits-come-learning-foreign-language Not only does learning a second language help your brain, but it also ..."
evolucious
"Why do people "snort" cocaine? Turns out that absorption through nasal tissues is ..."
evolucious
"I have to admit - I was unfamiliar with what a shrew was ..."
sciencegirl025
"Great article. It's definitely a great idea to keep an eye out for ..."
sciencegirl025
"Great article. It makes me think about what would happen if the malfunctioning ..."
explodingllama342
"There are actually an incredible amount of misconceptions about evolution. This piece explains ..."
explodingllama342
"It's amazing what damage to the brain can do, especially since effects vary ..."
explodingllama342
"That's awesome! The senses are amazing, especially when one considers their adaptability. http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/magazine-19524962 This ..."
explodingllama342
"It seems illogical to pay so much money for milk that has been ..."
explodingllama342
"Harvard is also tackling the issue of drug addictions. http://www.health.harvard.edu/newsweek/The_addicted_brain.htm Apparently, addictions may use the ..."
biorob
"This is a great post. I researched a little more about the "song ..."
biorob
"I think this is a very interesting article. Ironically, I think that having ..."
biorob
"Great article! It is amazing how we take advantage of our senses. I ..."
henroids
"Fear can bring the nature vs. nurture debate into play. How much of ..."
henroids
"According to http://www.foxnews.com/health/2012/11/07/science-explains-instant-attraction/ the brain decides a level of attraction to a person ..."
henroids
"I'll definitely keep an eye out for some of these foods next time ..."
ilikebioha
"I have had ear-worm plenty of times and I always wished I could ..."
ilikebioha
"You are right jk1234, "don't do drugs". Even if you just want to ..."
rawgdog
"Cool post hirschybar13! It's pretty neat how the reason why we remember songs ..."
troybolton
"How interesting! It is cool to think how natural substances can have ..."
troybolton
"Who would've known that something a show is based around is bad for ..."
inewitt
"Great article, it's always fun to speculate what might be out there. I ..."
inewitt
"Great article. There's been a lot of research into using bacteria as a ..."
thephilosopher
"In line with your inquiry into extraterrestrial life, Curiosity, the rover currently wandering ..."
thephilosopher
"It's incredibly unfortunate that people have conflated the morally suspect undertakings of government ..."
sciencegirl025
"It would make sense that color and presentation plays a role in the ..."
sciencegirl025
"Great article! It seems like we will have a back up plan in ..."
explodingllama342
"I find this pretty ironic because I hate the color orange and my ..."
explodingllama342
"I've heard things similar to this, and I've also heard that signing off ..."
explodingllama342
"I used to have REALLY sensitive teeth; even going out in the cold ..."
dwil
"I love hot chocolate so I think this is a very interesting article ..."
dwil
"I also have always thought that life on other planets can only exist ..."
dwil
"The concern of our energy future is a very important and troubling one. ..."
dwil
"The medical world can be a very, very odd and horrible place sometimes. ..."
dwil
"This is an interesting post about a very common yet annoying discomfort. I ..."
leahna
"Scientists have also started to find water on other planets too (http://www.time.com/time/health/article/0,8599,1642811,00.html) But when ..."
leahna
"Scientists have also started to find water on other planets too (http://www.time.com/time/health/article/0,8599,1642811,00.html) But when ..."
leahna
"This article also says that autoimmune diseases are on the rise in the ..."
biosasha11
"This was really interesting to read. Right now, researchers are drilling below Antarctica's ..."
henroids
"A very common myth about sleepwalking is that it is dangerous to wake ..."
arthenice
"Interesting article. Turns out grapefruits interact with enzymes in the intestines and effects ..."
arthenice
"Very interesting stuff. Colors do have a large impact on our appetite. Turns ..."
arthenice
"Great research. Tooth sensitivity is a problem that effects a lot of people. ..."
troybolton
"I guess I am going to start drinking from an Orange colored cup! ..."
troybolton
"Nice article Bg95! This is really cool finding. It is interesting to ..."
henroids
"Well I can't do a pull up, but I know some women who ..."
henroids
"Well if you don't have time to get a massage every week there ..."
henroids
"This is a real problem that needs to be taken seriously. There is ..."
hannahbanana
"Drivers can be tired and then add other distractions like playing with the ..."
hannahbanana
"Great article. I think its really important that even when research fails, it ..."
hannahbanana
"Wow!! What an improvement!!! HIV and AIDs are such sad epidemics, its great ..."
hannahbanana
"Wow! This is cool. Who knew you could beat jet lag!? I didn't! ..."
hannahbanana
"Weird! Grapefruit also is known for some great benefits like revving up the ..."
hannahbanana
"Wow this is a very interesting article! I never knew traits like altruism ..."
ilikebioha
"Evolucious--I am not a fan on insects either, but as said there are ..."
ilikebioha
"I was a little surprised when you said that the patients who got ..."
dwil
"I never thought having a bigger brain would be considered a bad thing, ..."
dwil
"This is a very interesting post on a very important and prevalent topic. ..."
jk1234
"Hippopotami have a 1:2789 brain to body ratio compared to 1:40 in humans. ..."
jk1234
"The progress made over the past years in the AIDS/HIV field has been ..."
explodingllama342
"This is amazing stuff. Anything that's an alternative to powerful pain meds is ..."
explodingllama342
"I think this is a great discovery. Personally, I'm of the mindset that ..."
explodingllama342
"This is a very serious issue. In addition to gadgets, the proper diet ..."
explodingllama342
"It's a shame more people don't know about how foods interact with drugs. ..."
evolucious
"Why are humans' brains so large? Psychologist Robin Dunbar believes that we ..."
evolucious
"While the majority of the population only needs 7-8 hours of sleep, teens ..."
evolucious
"This article is actually very appropriate, considering we just took a test on ..."
sayrest4
"This will prove very useful the next time I travel outside of my ..."
sayrest4
"This is very interesting! It has also been found that bees exhibit altruistic ..."
sayrest4
"Some animals, such as the Koala Bear, are quite the opposite of humans. ..."
sayrest4
"On top of falling asleep at the wheel, lack of sleep can impair ..."
jk1234
"Driving accidents are a huge problem in the world today. Along with drunk ..."
jk1234
"Wow, I would have never thought there was a connection between itchiness and ..."
rawgdog
"I agree with sciencegirl025, cool post! It's amazing how these bdelloids survive such ..."
rawgdog
"Awesome post biorob! I think it's so cool that people are able to ..."
sciencegirl025
"Great article! I especially find it interesting that the bdelloid has developed the ..."
sciencegirl025
"Wow! that's great! I recently read an article from the Huffington post about ..."
leahna
"Given that long-term exposure to stress is bad, it makes sense that stress ..."
leahna
"Though there are differences between men's and women's brains (http://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/brain-myths/201207/two-myths-and-three-facts-about-the-differences-in-men-and-womens-brains), it's very controversial ..."
thephilosopher
"According to the Alzheimer's Society, scientists have a pretty good understanding about how ..."
thephilosopher
"Interesting Post. I'm glad to see that the ~15 billion dollar massage industry ..."
biorob
"Great article! I agree with what sciencegirl025 is saying about how some animals ..."
biorob
"Great post! I agree with what explodingllama342 is saying about Post Traumatic Stree ..."
saysquad
"This article is very interesting. Even though women are not physically as strong ..."
saysquad
"Wow! This is super interesting. Now I am going to start getting massages ..."
biorob
"Great post jcfitzy! As state above, I cannot believe that the study of ..."
biorob
"Great post Rawgdawg! I do, however, agree with ilikebioha. While animals can imitate ..."
sciencegirl025
"Wow this is really great! Having the option to suppress memories, such as ..."
sciencegirl025
"Wow that is so interesting how dogs can share some of the same ..."
sciencegirl025
"Good article Rawdawggg. Not only can elephants "talk" but they also express emotion. ..."
explodingllama342
"Memory loss is terrible, and it freaks me out because Alzheimer's runs in ..."
explodingllama342
"This makes sense. I recently read a book called the Mindbody Prescription by ..."
explodingllama342
"This is very interesting. I actually read a book recently, called On Killing ..."
thephilosopher
"Very cool post! Interestingly, the two forms of blind mole rat examined in ..."
arthenice
"Great research and article! Allergies are very interesting according to the a study ..."
arthenice
"Very interesting. Some things that can also disrupt your sleep cycle are can ..."
arthenice
"Great information. Coffee is such a controversial drink, apparently it hurts your vision ..."
thephilosopher
"This is very interesting! It's truly incredible that gene sequencing technology has progressed ..."
arthenice
"Nice, the posterior insula is also triggered by social rejections according to this ..."
arthenice
"Great research, it's very interesting that physical activity and mental health have a ..."
sciencegirl025
"Great article. I didn't know that staying physically active could play a role ..."
sciencegirl025
"I actually find math really relaxing--quite the opposite of pain causing. But I ..."
henroids
"Suffering from pollen and sulfa allergies myself I know how bad it can ..."
henroids
"According to http://www.cnn.com/2012/10/05/health/snake-venom-pain-relief-time/index.html another painkiller was developed from venom. Ziconotide, a synthetic molecule ..."
henroids
"I don't hate math, english on the other hand.... This made me wonder ..."
henroids
"Just reading about yawning caused me to yawn! It really is contagious. According ..."
henroids
"Elephants aren't the only species able to communicate with and understand humans. Koko ..."
troybolton
"Nice post Explodingllama. I don't know if i personally experience tinnitus, but i ..."
troybolton
"This is interesting to see how an emotional response can end up triggering ..."
leahna
"This post was incredibly interesting. It's good to know that there are things ..."
saysquad
"bg95 this is a great article! Memory loss must be one of the ..."
saysquad
"This is a great article! Its so cool how scientist/police can discover the ..."
saysquad
"jcfitzy this is an incredible post. I cannot believe that such an unattractive ..."
saysquad
"Great job thephilosopher! This article on stem cells is super interesting. I had ..."
saysquad
"This is an amazing article! I never knew that you could predict an ..."
hannahbanana
"This is a great discovery. If this test is too late and you ..."
hannahbanana
"Wow! This is crazy!! I happen to be one of the few math ..."
hannahbanana
"Wow this is cool! http://web.mit.edu/newsoffice/2010/p53-1125.html is another article about solely p53. Maybe scientists ..."
hannahbanana
"Wow this is very interesting. I thought that dementia was random not preventable!! ..."
troybolton
"This is really interesting Biorob. Harvard did a study that showed how ..."
leahna
"I read an article about this before and I completely agree! I find ..."
evolucious
"Chimpanzees are another species that seem to have impressive language skills. In fact, ..."
evolucious
"Yes, it does seem that most students dislike math - and now with ..."
dwil
"This is really cool because there are countless people who have issues with ..."
dwil
"This is a great discovery. Any breakthrough that can help predict a severe ..."
dwil
"While humans are usually thought to be the only species capable of creating ..."
dwil
"I hate math too. Maybe if I show this post to my doctor ..."
dwil
"Interesting post. While studying animals for human medical benefit is usually something that ..."
bg95
"In a way, this article relates to the article by rawgdog about the ..."
bg95
"How do scientists know that the elephant has no understanding of the meaning ..."
Sleep Deprived
"An interesting, informative and helpful perspective on a complex and not-well-understood disorder. Thanks ..."
ilikebioha
"As an animal lover, i know i would love to have a pet ..."
ilikebioha
"I do agree and think that there is a correlation between the way ..."
ilikebioha
"I've always known yawning is contagious but I never new why. After looking ..."
ilikebioha
"I agree with troybolton. I think in order for stem cell therapy ..."
ilikebioha
"I am not trying to denounce Koshiks skill, but just because he can ..."
inewitt
"This is a good read jcfitzy. One of the biggest problems with harnessing ..."
inewitt
"Good article. Now scientists just need to find a way to reverse deafness ..."
inewitt
"In addition to the many harmful side effects of morphine that sayrest4 pointed ..."
inewitt
"Good article biorob. Scientists recently looked at the effects of alcohol on forgetting ..."
inewitt
"Really interesting article rawgdog. Elephants aren't the only animals who have begun to ..."
jk1234
"Progress on cancer treatment options has been improving a lot lately. Using magnets ..."
jk1234
"Elephants using their trunks to make different sounds is incredible. Elephants also use ..."
jk1234
"I never realized sleep walking was such a huge issue. Another issue related ..."
jk1234
"Diagnosing allergies is extremely important in order to prevent any incidents of anaphylaxis. ..."
jk1234
"Venom is becoming popular in medicinal research. The black mamba venom is now ..."
rawgdog
"Cool post jcfitzy! Your post reminded me a lot of an article I ..."
rawgdog
"Cool post henroids! Interestingly, magnetic treatment has also been utilized to relieve Epilepsy. ..."
sayrest4
"If these findings are true, then it could lead to the improvement of ..."
saysquad
"Hirshybar, this article is really cool. I never knew that yawning was actually ..."
saysquad
"Henroids,this is a very intriguing article! I knew magnets were not just for ..."
sayrest4
"This is very informative. Most people attribute the word stress with anxiety or ..."
sayrest4
"This is very interesting, and is just one way in which the brain ..."
sayrest4
"There is an article which suggests that this kind of technique can be ..."
sayrest4
"Nice article! I wonder how this plays into the theory that animals yawn ..."
hannahbanana
"This is a very interesting article. As I teen, I am always told ..."
hannahbanana
"Here is a link with some more help http://kidshealth.org/parent/growth/sleep/sleepwalking.html# "
hannahbanana
"Great article! Although, it did make me a little uneasy: I have slept ..."
biorob
"It is very interesting that researchers may be able to find a pain ..."
biorob
"It is crazy to think that coffee, which is one of the most ..."
evolucious
"I have bumped my head more than a few times.Luckily, the human brain ..."
evolucious
"Personally, I would rather lose some bitter-tasting fruit than have to endure mosquitos ..."
evolucious
"I have never experienced anything like this and hope I never will. However, ..."
evolucious
"I know that when spring comes around, I start sneezing and wheezing. But ..."
evolucious
"Well, try some tea instead! Green tea is often touted for its health ..."
bg95
"While I agree it's important to consider the risk of Exfoliation Glaucoma before ..."
troybolton
"This is interesting. I completely agree with the fact that we need ..."
troybolton
"I think I need to stop drinking so much coffee! I can understand ..."
dwil
"Wow! This post is one of the most interesting I have read to ..."
dwil
"Thanks! That is all very useful information and on a very important topic. ..."
thephilosopher
"Interesting! This is a little frightening, to be honest. A friend of mine ..."
thephilosopher
"Great article, Rawgdog. Morphine and other opiate derivatives have long been the best ..."
ilikebioha
"I also think that stress is necessary in peoples lives. This article ..."
ilikebioha
"The article states that the disease is spread via human to human contact. ..."
troybolton
"I personally feel that we should go forth and test more into stem ..."
troybolton
"Cool! After reading this article I think that my dad should see a ..."
troybolton
"I find this very interesting! It is good to know that we ..."
hannahbanana
"This is an interesting article and like explodingllama342 it doesn't shock me. It ..."
hannahbanana
"Wow! This post was very interesting! I do think that every person's DNA ..."
inewitt
"This is a very good development, since it's becoming apparent that hearing loss ..."
saysquad
"This article is very sad. Nobody really knows the true cause of premature ..."
saysquad
"Biorob! This article is extremely intriguing. As well as having very thick skulls ..."
arthenice
"Interesting article, I hate mosquitoes but I never realized how important they were ..."
arthenice
"Interesting information. Not only does a lack of sleep leave you feeling tired ..."
henroids
"Great post Explodingllama! The idea of having a small delivery device that can ..."
henroids
"It is a shame that the Great Barrier Reef is shrinking, but not ..."
rawgdog
"Cool post! I think if you generalize the concept portrayed in this article, ..."
rawgdog
"Wow! This discovery is very intriguing. Though I truly abhor mosquitoes, my personal ..."
sciencegirl025
"Very interesting article, it's studies like this which makes me appreciate things otherwise ..."
sciencegirl025
"Very interesting article, especially how many teenagers can relate to shifting sleep schedules! ..."
sayrest4
"It is very unfortunate that the Great Barrier Reef is in danger. On ..."
jk1234
"The Democratic Republic of the Congo, along with most other African countries, has ..."
jk1234
"It's terrifying how brain trauma cases in the NFL has become such a ..."
sayrest4
"The information in this article is very interesting when applied to human skulls. ..."
inewitt
"In fact, the number of crown of thorns starfish has become so great ..."
biorob
"Very interesting article and story. It is scary to think about the viruses ..."
biorob
"This is a very interesting article! It is such a shame that the ..."
bg95
"I find this post interesting because I always assumed the levels of stress ..."
leahna
"This is so interesting! It appears the brain is definitely wired to enjoy certain ..."
explodingllama342
"The heart is probably one of the most taxed organs when one is ..."
explodingllama342
"This is fascinating. It think research like this, which will help us understand ..."
biosasha11
"I think that the new stem cell found in the brain is already ..."
biosasha11
"This is a very interesting post. It's crazy that some babies have to ..."
evolucious
"Nice post! Bowerbirds aren't the only intelligent animals with courtship displays, but they ..."
evolucious
"Interesting, but controversial topic. While infants being born with opiate addictions is not ..."
Mont3rros4
"Thank for using one of my photos Mont3rros4 "
Ellespot
"according to an animal rights group.....perhaps you should take a look at some ..."
nyrtac2012
"Great advice! It is always a good idea to start the day with ..."
nyrtac2012
"Wow, this makes a lot of sense. We have always been told that ..."
sweetasglucose
"WOW! Bowerbirds sound like intelligent creatures. Many types of birds are very intelligent. ..."
aminoalix
"OY! This is a crazy post, especially since I do not like to ..."
sweetasglucose
"Such a useful article! I often want to tune people out, and now ..."
aminoalix
"This is a really interesting post, especially since I tend to zone out ..."
sweetasglucose
"It was great to see an article about polar bears. I feel as ..."
sweetasglucose
"Wow! It's nice to FINALLY have a reason as to why to eat ..."
Nima
"Someone pointed me to this post, and I enjoyed your summary of this ..."
buddhabear28
"In response to jackalantern926's comment, that is very disgusting and very troublesome. In ..."
buddhabear28
"12whiteal, I think precocious puberty is something to worry about because of its ..."
buddhabear28
"Gababoutbio, I have to agree that abortions may alter the statistics of teenage ..."
buddhabear28
"This article is very interesting in that it makes me wonder why a ..."
buddhabear28
"Honestly, I am slightly confused by this article. It doesn't make sense to ..."
jackalantern926
"Wow this is so interesting! I did some more research on CXCR4 genes ..."
jackalantern926
"This post has definitely inspired me to formulate my own escape plan from ..."
sweetasglucose
"Omg! yes! We MUST hope for more research about this disorder. Thanks for ..."
sweetasglucose
"Whether or not obseity is genetic or the fault of the human is ..."
k2l2
"I love this post too rebecafe12! It is really relavent to me, because ..."
k2l2
"It is interesting to me that DNA can play such a role in ..."
12whiteal
"Wow cool article Nicleus2! It makes a lot of sense that there is ..."
carlybio12
"thats so weird! Something interesting about our taste buds is that the same ..."
carlybio12
"that is so interesting! similarly to how people blame fat people for "eating ..."
lp719
"I never heard about statins until this article! After reading this, I became ..."
lp719
"This article really interested me because I have always been skeptical of effective ..."
gababoutbio
"Did you know that it is not only about their diets but also ..."
gababoutbio
"Did you know that they also found better ways to find cancer in ..."
nicleus2
"This article immediately reached me because I too have such horrific spring allergies. ..."
nicleus2
"This article upset me a little because I myself am a lover of ..."
rebecafa12
"I love this post. People are always shocked to hear that I'm ..."
buddhabear28
"Lagis2012 and carlybio 2012 your points were the first two things that came ..."
buddhabear28
"This article is not only scary but upsetting, seeing as though I am ..."
lp719
"I almost always procrastinate, especially on the weekends. Throughout my high school career, ..."
lp719
"As a huge red meat lover, this article really scared me. I consider ..."
aminoalix
"I was shocked when I read this because I had no idea that ..."
aminoalix
"Wow! I am really glad that I am not male because I love ..."
sar418
"I have allergies year around that get worst in the fall and spring. ..."
sar418
"I classify myself as the master of procrastination. I also do not work ..."
carlybio12
"This is really interesting! Another article shows that there is a direct correlation ..."
carlybio12
"Eating too much sugar can also harm the balance of estrogen and testosterone ..."
carlybio12
"That is so interesting! Trees really are smart...did you know that "some trees ..."
carlybio12
"I don't have any allergies but you are not alone! "The Food and ..."
carlybio12
"I consider myself to be one of the "20% of people that identify ..."
biologiamaster
"I had once heard about a study that tried to determine weather or ..."
biologiamaster
"Any post relating to nutrition is generally interesting to me. It seems ..."
gababoutbio
"Did you know, that at Manhasset hospital they are using iphone to detect ..."
gababoutbio
"Here are some ways to alleviate stress! 1. Get sleep 2. Excercise 3. ..."
gababoutbio
"While white sugar can lead to such bad things, raw sugar cane is ..."
gababoutbio
"WE learned about how genes could be turned on and off and that ..."
gababoutbio
"An article i read said that "Fear of losing autonomy" is another reason ..."
nyrtac2012
"Great article! I like how you discuss the different types of procrastination, and ..."
lagis2012
"I find that a lot of students study and do other things at ..."
maureen hanvey
"try aeroponically grown wheatgrass. i have been taking it for 12 years. ..."
12whiteal
"That is so interesting k212!I never knew that disgust is actually disease avoidance ..."
12whiteal
"This is such a cool article paige2994! I never knew that hypnosis can ..."
sar418
"This is really interesting to me, because I lost a family friend to ..."
sar418
"Wow! That's so weird! I have horrible allergies most of the year, but ..."
nicleus2
"I found this incredibly interesting and innovative! This prompted me to look up ..."
nicleus2
"I found this post to be very interesting, but I feel that the ..."
biologiamaster
"It is interesting to note that many doctors have wide variations of what ..."
biologiamaster
"This post reminded me of an article in the NY times, "An Immune ..."
buddhabear28
"Though this interesting, you state this increasing your daily dosage of vitamin D ..."
buddhabear28
"I totally agree and I think that "poppin' pills" is severely unhealthy because ..."
gambibambi
"That's so interesting! Some researchers have proposed that vitamin d deficieny could be ..."
gambibambi
"Wow this is so interesting! Maybe I'm just wired to have a bad ..."
ayl103
"I think it is beneficial for people to go to the chiropractor and ..."
lagis2012
"Pasta is my favorite food! I would definitely have to give serious ..."
lagis2012
"Thats really interesting! I was curious and looked more into the topic. ..."
nyrtac2012
"That is really interesting. I always knew that scientists believe sharks to be ..."
ayl103
"Wow, that is really interesting that vitamin D may help reduce the likelihood ..."
idolph94
"I don't know if this is exactly considered "evolution" as Darwin put it. ..."
idolph94
"I can definitely see this as a controversial topic, especially since so many ..."
jackalantern926
"I also agree that yoga can be detrimental, if not done properly. I ..."
jackalantern926
"Hey sweetasglucose! I thought that being able to blame parents for allergies was ..."
lp719
"As an avid practitioner of hot yoga, I was very disappointed when I ..."
lp719
"Before reading this article, I had never assumed that cancer and glucose were ..."
gababoutbio
"This idea that you're talking about has a name, i actually know people ..."
aminoalix
"This is a really interesting topic, as I have never learned much about ..."
gababoutbio
"two things 1. did you know that babies born without eyes get prosthetic ..."
aminoalix
"I knew who had written this post before even looking for the author! ..."
carlybio12
"I too dislike yoga, but i disagree. I think that yoga (and meditation) ..."
Pasta :: New York Times :: Discovery Channel :: NRC :: … [Updated] « Sander Huisman
"[...] by the http://www.rendabordo.com Also covered by the http://ceticismo.net Also covered by the ..."
lagis2012
"While I agree with you, I see the positive effects of yog in ..."
sweetasglucose
"My goodness! This was a shocking and sad blog. I knew about heart ..."
sweetasglucose
"Fortunately, I have never had a problem falling asleep. I do hope however, ..."
sweetasglucose
"Oh my goodness, I do remember that SAT reading passage. I am so ..."
sweetasglucose
"1,500 years doesn't seem very long, but it is true we will be ..."
sweetasglucose
"As soon as I saw "stem cell" I knew I had to read ..."
sar418
"This is crazy! I understand the need to ahead of a virus, but ..."
sar418
"Wow, it's amazing how much we are advancing with technology. At Hofstra Medical ..."
12whiteal
"Thats so cool rebecafa12! There are alot of cool things going on with ..."
buddhabear28
"I wonder if at the end of your article you meant "virgin birth ..."
buddhabear28
"I am in complete agreement with this article because I don't think taking ..."
nicleus2
"What a great article! I am a firm believe of only taking medicine ..."
nicleus2
"Caffeine is undoubtedly bad for you. It is a drug that undoubtedly effects ..."
nicleus2
"I was so interested by this article, that I decided to do further ..."
nicleus2
"I find it interesting how certain organisms die from stress. Although stress ..."
nicleus2
"I found this article very interesting and at the same time disgusting. It ..."
12whiteal
"cool article michael2012! I never knew that turtles all hatched together let alone ..."
carlybio12
"Although a stressful situation probably won't kill you...it can make your hair turn ..."
carlybio12
"Did you know that coffee can also be helpful in making an argument ..."
mrmoz55
"The benefits of a good nights sleep are essentially vital for the human ..."
ddecam198
"This is a very interesting study. I have always thought it a bit ..."
biologiamaster
"I completely agree with the NYU professor who states that doing nothing can ..."
biologiamaster
"It is interesting that a suppressed immune system lead to the death of ..."
biologiamaster
"The development of an iPhone capable of diagnosing bacterial infections is encouraging to ..."
biologiamaster
"While at first glance E-cigs may seem no less harmful than cigarettes, there ..."
biologiamaster
"A few years ago i remember reading about how the TSH reference range ..."
ayl103
"I think its awesome that scientist are getting closer to finding a cure ..."
ayl103
"I totally agree that stress has some serious effects on peoples body and ..."
aminoalix
"I for one do not enjoy drinking coffee. Unlike myself, many individuals agree ..."
aminoalix
"WOW! That feature on a phone would be awesome! However, have you heard the ..."
lp719
"I was really interested by this article because I notice that when I ..."
lp719
"This article immediately caught my attention because as an avid coffee drinker, I ..."
gambibambi
"Wow Michael, that's so cool how different levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide ..."
gababoutbio
"It's really amazing what iphones can do! Medically the iphone released a app ..."
gababoutbio
"while stress may not kill us humans, it absolutely alters our personalities. Here ..."
lagis2012
"I found your article very interesting so I did a little more research ..."
lagis2012
"This is really interesting! I wonder if this is true for other ..."
sweetasglucose
"love the title and I love the picture! It totally captures 1st semester ..."
12whiteal
"This is so cool K212, I was wondering why siri and GPS systems ..."
12whiteal
"Wow yazzairbik1294 this is such a cool article! I never knew that sometimes ..."
sar418
"I myself understood a language other than English when I was younger, but ..."
sar418
"Wow! That's so weird, I never realized it, but that is completely true! ..."
idolph94
"When I first glanced at the article, I immediately read that these E-Cigarettes ..."
buddhabear28
"I agree with nicleus2* the most gag inducing sound* "
buddhabear28
"I agree with lp719 that finger nails down a chalk board is pretty ..."
buddhabear28
"I agree with lp719 in that E-cigarettes can't be that great an alternative ..."
mrmoz55
"http://www.dynamicgreens.com/wheatgrass-benefits-of-wheatgrass.html "
ayl103
"I can't believe that the diabetes population has DOUBLED over the last 10 ..."
ayl103
"Wow, that is a really interesting experiment. I never thought kids would have ..."
mrmoz55
"I completely agree with this study, that there are no significant health benefits ..."
lp719
"As a child, I always thought the idea of being hypnotized was really ..."
lp719
"This article caught my attention because I am completely against smoking. When I ..."
jackalantern926
"Wow gambibambi this is so cool! Did you know that mutations of "the ..."
sweetasglucose
"Wow! Exercise does leave a huge impact on peoples lives. I learned from ..."
nicleus2
"This post immediately caught my attention before I even read it. I can't ..."
nicleus2
"I can really relate to this article, because I have noticed that whenever ..."
nicleus2
"In your post, you talked about superbugs and how they get stronger the ..."
nicleus2
"Although I could not totally relate to this article, due to the fact ..."
nicleus2
"I found this post much more interesting than disgusting. In fact, it prompted ..."
carlybio12
"Something else interesting to think about is whether or not different parts of ..."
carlybio12
"Another interesting thing about sleep is that obesity and sleep deprivation are somewhat ..."
biologiamaster
"http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2011/09/110912092554.htm. Another thing i have always considered when getting a good nights sleep is ..."
biologiamaster
"Its refreshing to see that dietary supplements are being given a second look, ..."
biologiamaster
"The decline of the bee population seems like it would have noticeable effect ..."
biologiamaster
"Over the summer i interned with a doctor who used shark cartilage injections ..."
biologiamaster
"Awhile ago i came across an article (http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2011/08/killing-beneficial-bacteria/) that warned of long term ..."
biologiamaster
"On the same note, researchers have found that carotenoid in isolated supplement (such ..."
aminoalix
"This seems extremely unfortunate!! In reality, 5% of 832 babies diagnosed with autism ..."
aminoalix
"WHOA! I feel like we have talked about this before. Even though your ..."
jackalantern926
"This is so interesting! Did you know that Broccoli is great for detoxification? ..."
jackalantern926
"This is absolutely disgusting. However, did you know that praying mantis are also ..."
sweetasglucose
"This is by far the most disgusting thing I have read in a ..."
gababoutbio
"Wow, I am truly disgusted but yet intrigued at the same time! I ..."
gababoutbio
"Very interesting to hear this. Did you know that Shark fin is a ..."
lagis2012
"Thinking on your question, I believe doing different types of studying and activities ..."
lagis2012
"I find that being able to get a good nights sleep in a ..."
gambibambi
"YES!!! I had been reading about this over the summer in an old ..."
aminoalix
"Due to your love of sharks, I was not surprised to see you ..."
12whiteal
"Great article sar418. I personally dislike sharks and I never knew that they ..."
12whiteal
"Wow Michael 2012, this is such an interesting article because the debate over ..."
buddhabear28
"I think its interesting that a lot is being done to revive the ..."
gambibambi
"Yes an no Gab. Yes: this doesn't perfectly fit homosexual attraction because homosexuals ..."
yazzairbik1294
"Love the title! After doing some more research, I found that many sources ..."
yazzairbik1294
"Cool article--I've heard of this, but never actually found anything on it, thanks ..."
ayl103
"That is so interesting! I always wondered why I woke up before my ..."
buddhabear28
"I agree with grexthebiodino in that it’s really unfortunate for the Jensen Farmers ..."
nicleus2
"I found this article very interesting and can really relate to how laughter ..."
ayl103
"That is so sad that Koalas may become extinct because of Chlamydia! Apparently ..."
lp719
"I really enjoyed reading this because I always wonder why I wake up ..."
lp719
"This article really interested me because cantaloupe is one of my favorite fruits, ..."
aminoalix
"Wow! I didn't know naked mole rats were so necessary in our medical ..."
biologiamaster
"Not only does laughter release endorphins it also has measurable health benefits! Researchers at ..."
biologiamaster
"Its interesting that Doctor Oz reccomends Canola Oil as a "healthy fat". ..."
gababoutbio
"I decided to further my comment haha: Chocolate is also thought to inhibit ..."
gababoutbio
"2 corrections sorry!! hahah **heterosexual**** and here is a link to the specific ..."
sweetasglucose
"THAT Naked Mole Rat does NOT look like Rufus!!!! Disney's Kim Possible is VERY ..."
sweetasglucose
"hahahahaha i "
sweetasglucose
"Great Article!! Plus, that koala is TOO CUTE! "
lagis2012
"Its interesting, because as I read this, I thought of other outbreaks dealing ..."
mrmoz55
"This post really sparks my attention because I laugh many times day. I ..."
gababoutbio
"While this explains so much about heterogenous attractions it still does not fully ..."
grexthebiodino
"I feel so bad for the farmers! This ABC News article gives more ..."
gambibambi
"This always happens to me when I'm doing research for big papers and ..."
grexthebiodino
"This is really interesting and made me want to the topic of laughter ..."
lagis2012
"I thought that was so interesting! I researched how dopamine affects teen ..."
carlybio12
"This post is so interesting! I came across another article focusing on embarrassment- ..."
carlybio12
"It is interesting how you said laughter acts as a painkiller, because laughter ..."
sweetasglucose
"Great blog clumsy girl! Hey! Did you know that when you are embarrassed, ..."
sweetasglucose
"This is really interesting, and the part about laughter being a bond to ..."